Middle School Biology (3/3): Genetics, Evolution, and Natural Selection
In this final post of my biology series, I explore genes, evolution, and natural selection. I was amazed to learn that broccoli, kale, and cabbage all come from the same plant. These lessons connect deeply to both health and my work in AI and animal communication.
In this final post of my Middle School Biology series, I’m wrapping up my notes from Khan Academy’s Middle School Biology course. These last three units cover some of the most fascinating topics in biology: genetics, evolution, and natural selection.
These concepts are also highly relevant to my work at Earth Species Project, where we study patterns of communication across species. Evolutionary relationships and genetic variation often underlie the signals animals use to survive, reproduce, and thrive in changing environments.
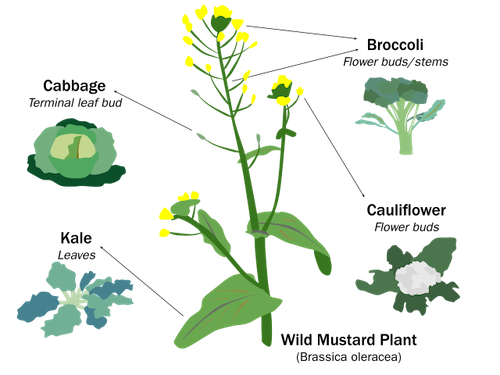
One moment that really struck me while studying these units was learning that vegetables like cabbage, kale, broccoli, and cauliflower all come from the same plant species: Brassica oleracea, or wild mustard. All of these are incredibly healthy, and they happen to be vegetables I eat almost every day for my health!
Unit 7: Inheritance and variation
- Chromosomes
- genes pass traits from parents to offsprings
- chromosomes in the nucleus contain DNA
- chromosomes come in pairs called homologous chromosomes (23 pairs for human)
- alleles are different versions of the gene
- karyotype — view of chromosomes
- Genes, proteins, and traits
- DNA is made up of nucleotides (A, T, C, G)
- gene is a specific stretch of nucleotides
- nucleotides -> amino acids -> 3D structure of proteins
- GFP (green fluorescent protein) can be attached to other cells to visualize
- Mutations
- three nucleotides correspond to an amino acid
- mutations happen when DNA is copied, or by environmental factors
- Reproduction and genetic variation
- haploid vs diploid -> 2 haploid gametes fuse to create diploid offsprings
- haploid gametes -> one set of chromosomes
- variations of offspring
- allele(s) -> versions of a gene
- genotype vs phenotype
- homozygous (same alleles) vs heterozygous (different alleles)
Unit 8: Evolution
- Evolution and common ancestry
- Genetic variation (including sexual reproduction) over time causes evolution
- 10,000+ species of birds
- All modern bird species evolved from the common ancestor
- A species' lineage is its series of ancestral species
- The fossil record
- fossil: preserved evidence of organisms that lived in the past (in sedimentary rocks)
- Estimating the age of fossils: analyze the layers, or use radiometric dating (measure the atom decay)
- Earth's fossil record: consists of all the fossils found on Earth along with their relative ages
- The Cambrian explosion -> rapid increase of complex organisms, happened ~540 million years ago
- Evidence of evolution: anatomy
- anatomical/physical features of organism for evidence of evolution
- Homologous --> two species share similar features (e.g., human arms and bird wings)
- Analogous --> two similar features that evolved independently (e.g., bird and butterfly wings)
- Evidence of evolution: embryology
- Human embryo has a tail-like structure, so do other vertebrates
Unit 9: Natural and artificial selection
-
Natural selection
- Example: peppered moths, initially white, but got darker and darker during the industrial revolution
- Recently white peppered moths are returning
-
Adaptation and environmental change
- Beak depth of Galápagos finches became longer due to a draught within two years
-
Artificial selection and domestication
- Domestication of wolves, and different breeds of dogs
- Wild pigs -> farmed pigs, produces ar supermarkets
- Artificial selection of the wild mustard plant led to: cabbage, kale, broccoli, cauliflower, and brussels sprouts